In our technology-driven world, digital literacy is no longer a skill exclusive to office workers or tech-savvy professionals. It is rapidly becoming a necessity for frontline and essential workers as well. From healthcare staff using electronic health records (EHRs) to retail associates handling digital point-of-sale systems, the ability to navigate basic technology is now an essential part of the job. Even roles that were once purely analog now demand digital skills: today’s truck drivers, for example, must navigate technologies like electronic logging devices (ELDs), GPS systems, and other digital tools essential to their jobs.
While some roles still require little to no digital literacy, the landscape is shifting. Organizations that prioritize digital upskilling for their frontline workforce will not only boost productivity but also enhance employee satisfaction and improve customer service.
The Expanding Digital Literacy Imperative
Digital literacy refers to the ability to find, evaluate, use, and communicate information through digital platforms. For years, it was viewed as a must-have skill in white-collar roles, but digital tools are now deeply integrated into frontline work.
By 2030, the World Economic Forum (WEF) estimates that more than 1 billion people will need reskilling due to technological advancements and shifts in the global economy. This includes frontline workers who, historically, have relied more on manual skills. The pandemic accelerated this trend, as many frontline employees were required to use mobile scheduling apps, digital communication tools, and e-learning platforms to stay connected and informed.
Why Digital Literacy Matters for Frontline Workers:
- Increased Efficiency: Digitally literate workers can handle inventory management, scheduling, and customer interactions faster and more accurately.
- Improved Safety and Compliance: In industries like manufacturing and healthcare, using digital tools correctly ensures adherence to safety protocols and regulatory compliance.
- Better Communication: Messaging apps, video conferencing, and digital dashboards keep frontline workers aligned with their teams and management.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Tech-savvy frontline employees can offer faster service, manage orders efficiently, and troubleshoot basic technical issues, boosting customer satisfaction.
Examples of Digital Literacy in Frontline and Essential Roles
1. Healthcare: Digital Patient Records and Telemedicine
The healthcare sector has undergone significant digital transformation. Nurses, doctors, and administrative staff now rely heavily on:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs) for patient documentation and charting.
- Telehealth platforms for remote patient care.
- Digital scheduling systems to manage appointments and resources.
Without basic digital literacy, healthcare professionals risk making costly errors or being unable to use life-saving technology efficiently.
2. Retail: Point-of-Sale (POS) and Inventory Systems
Retail employees are increasingly required to use:
- POS terminals with touchscreens and digital payment systems.
- Inventory management software to track stock levels and sales.
- E-commerce platforms to fulfill online orders and assist customers.
Workers with low digital literacy may struggle to process payments, check stock, or troubleshoot minor technical issues, leading to frustrated customers and lost sales.
3. Logistics and Warehousing: Digital Tracking and Fleet Management
In the logistics sector, frontline workers must be comfortable using:
- Barcode scanners and RFID technology for inventory management.
- GPS and fleet tracking systems to monitor deliveries.
- Mobile apps for logging hours or communicating with dispatch teams.
Lack of digital proficiency can lead to delays, lost shipments, and errors in order fulfillment.
4. Hospitality and Food Services: Mobile Ordering and Scheduling
In restaurants and hotels, digital literacy is now essential for:
- Mobile ordering and payment platforms.
- Digital reservation and booking systems.
- Employee scheduling apps to manage shifts and communication.
Workers who can’t adapt to these digital tools may struggle to meet customer expectations or work efficiently.
Roles Where Digital Literacy Is Still Minimal
While digital literacy is becoming widespread, there are still some roles where it remains less critical. These include roles like traditional farm laborers, construction workers and housekeeping or cleaning staff. Many roles involving physical labor still require some tech proficiency along with manual skills.
However, even in these fields, digital literacy is gradually creeping in as organizations adopt scheduling apps, training platforms, and task management software.
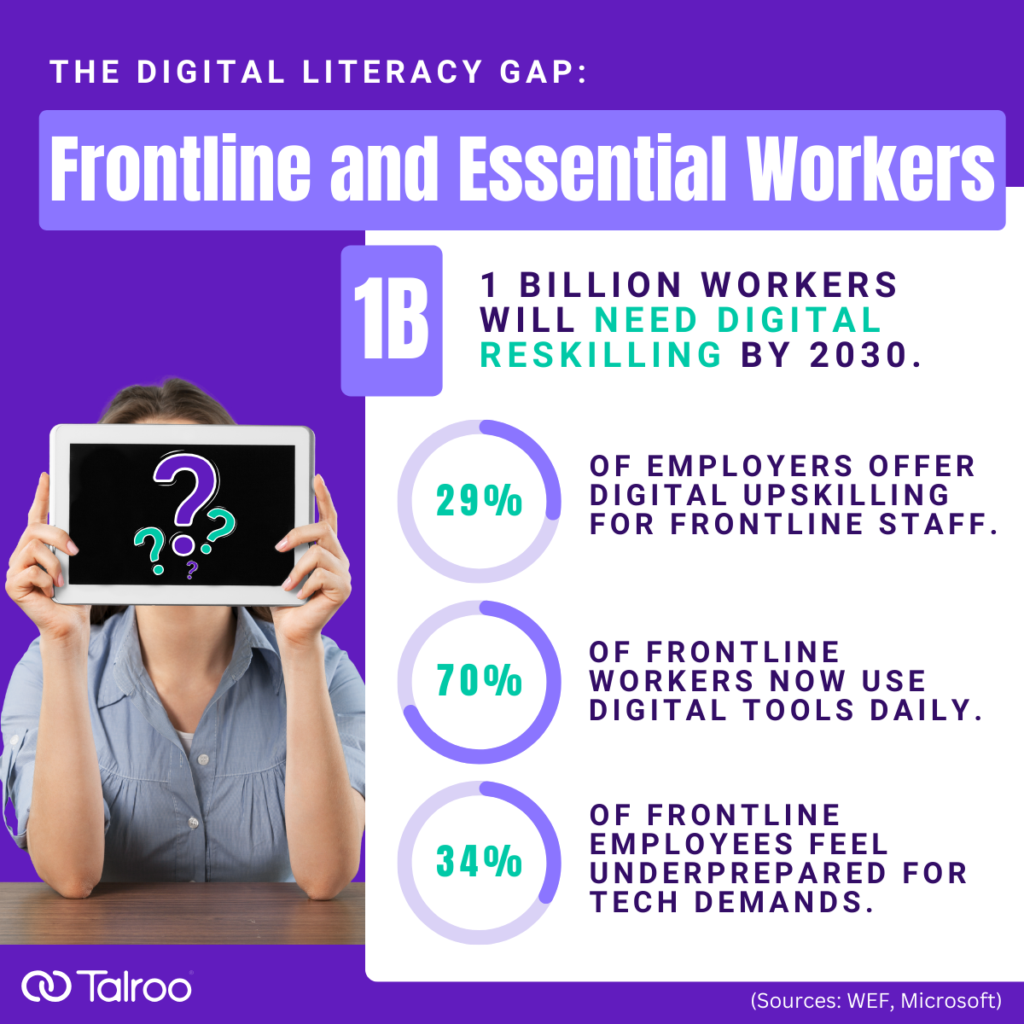
Bridging the Digital Literacy Gap
1. Skills-Based Hiring
Focus on digital literacy when building your workforce, highlight and hire workers with the skills needed to build the digital expertise. Don’t focus only on those with prior experience with your platforms and instead use skills-based hiring to build your workforce, finding those with the skills and propensity to learn and grow.
2. Upskilling and On-the-Job Training
Employers should offer digital literacy training programs specifically designed for frontline workers. This may include:
- Basic tech skills workshops (e.g., using POS systems or mobile apps).
- Microlearning modules delivered via mobile-friendly platforms.
- Gamified learning experiences to engage and motivate employees.
3. User-Friendly Technology
Companies should prioritize intuitive and accessible technology. Tools with simple interfaces, clear instructions, and visual cues reduce the learning curve and make it easier for frontline workers to adopt them.
4. Digital Mentorship and Peer Support
Creating digital literacy mentorship programs can help less tech-savvy employees learn from their peers.
- Pairing digitally literate employees with those who need support promotes collaborative learning.
- Encouraging peer-to-peer knowledge sharing builds confidence and competence.
5. Equitable Access to Technology
Frontline and essential workers often lack access to personal devices or high-speed internet. Employers can bridge this gap by:
- Providing company-owned tablets or smartphones.
- Offering on-site tech resources (e.g., kiosks or terminals for digital tasks).
- Ensuring that training materials are available offline.
The Future of Digital Literacy for Frontline Workers
As automation and digital transformation continue, digital literacy will become an essential skill across all industries. Even roles that traditionally relied on physical skills will require employees to interact with digital tools.
Organizations that invest in digital upskilling will benefit from:
- Higher productivity and accuracy.
- Reduced error rates and compliance risks.
- Greater employee engagement and retention.
For frontline and essential workers, digital literacy is no longer a bonus—it’s a fundamental job requirement. Companies that support their workforce with accessible training and user-friendly technology will build a more resilient and adaptable frontline team.
Digital literacy is no longer confined to office jobs. Frontline and essential workers increasingly rely on technology to perform their duties effectively. While some roles remain less dependent on digital skills, most frontline employees need basic proficiency with digital tools to succeed.
By investing in training, mentorship, and accessible technology, organizations can empower their workforce, boost productivity, and enhance the customer experience—making digital literacy a vital part of modern frontline success.



